The common types of chronic joint pain are as a result of arthritis. This is a common disorder that affects the joints causing inflammation and pain thereby making it difficult for one to move or stay active. There are very many types of arthritis each with its different causes, symptoms, and treatments.
It mostly affects adults but can also affect children of any age. The following are the four common types of arthritis, their causes, symptoms, and treatments.
1. Osteoarthritis
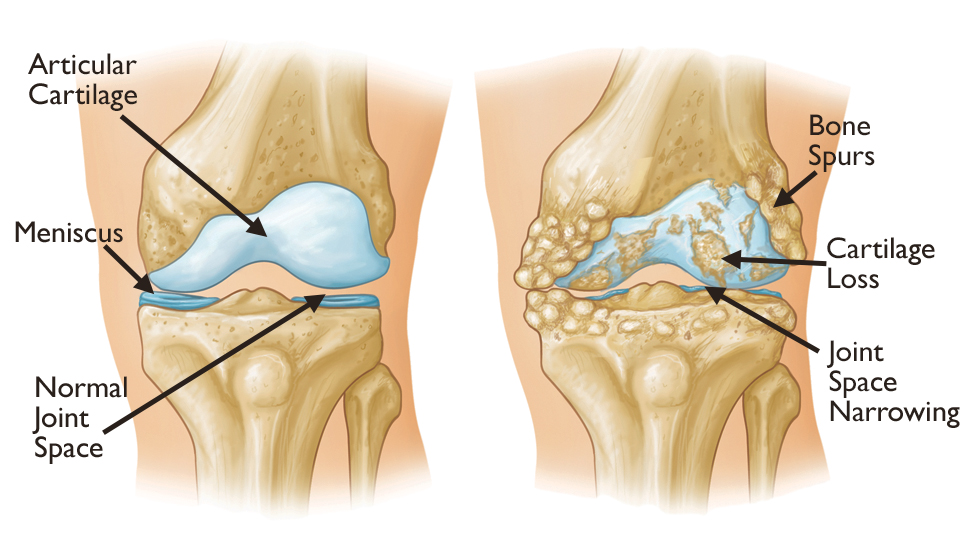
Most people are usually affected by this type of joint pain compared to any other form of arthritis. It is the “wearing” and “tearing” that occurs when your joints have been overused. In most cases, it is a result of aging. However, it can also occur when you have joint injuries or you have obesity. These conditions can put extra stress on your joints.
It commonly affects the feet, spine, knees, and hips. It causes the affected joint to hurt but does not cause fatigue or you do not feel sick like other types of arthritis.
When you are affected by osteoarthritis, the body shock absorber is lost. The slippery material is the cartilage, which covers the end of the bones and breaks down gradually. The damaged cartilage then moves to be painful. The roughened cartilage on the surface of the bones will rub together and a grating sound may be heard.
Painful bumps or spurs may also be experienced at the end of the bones. This usually happens on the feet or fingers.
Symptoms
- Pain when walking
- Morning sickness that may last less than 30 minutes.
- You experience trouble when dressing, gripping things, bending over and squatting. This depends on which joints are involved.
- You experience deep aching pain
- Stiffness when you are resting.
- Your joint may also be warm when you touch it, unable to be moved in a full range motion, and swollen and harder to move.
Osteoarthritis cannot be reversed but some medications help in relieving pain. You can use
- Oral pain relievers for example Acetaminophen. They help in reducing pain.
- Topical pain relievers include creams, gel, and patches. They numb the joint area thereby providing pain relief.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as naproxen and ibuprofen help in reducing pain and swelling.
You can also manage it by doing exercises, managing your weight, and eating healthy food. Surgery may be done when the case is severe.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
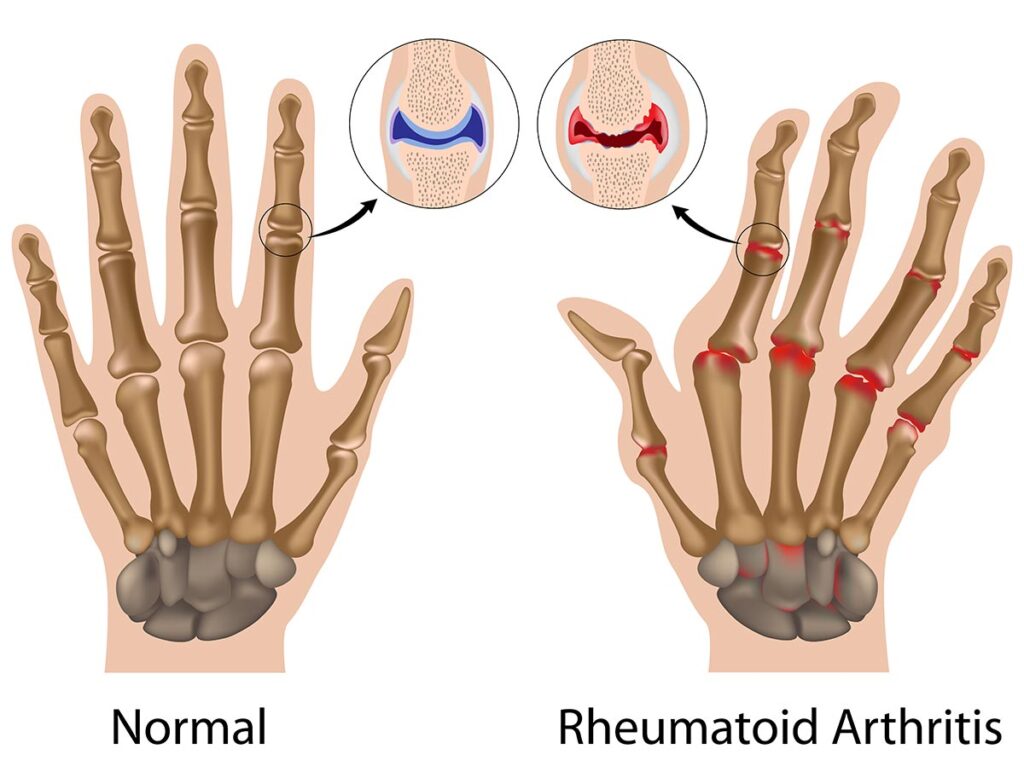
It is an autoimmune disease meaning that the immune system attacks the parts of the body, especially the joints. This attack leads to inflammation. This can cause severe joint damage in case it is not treated.
1 out of every 5 people who suffer from rheumatoid arthritis normally gets lumps on their skin. These lumps are known as rheumatoid nodules and they form over the joint areas such as elbows, heels, or knuckles.
The causes of RA are still not yet known by doctors but some experts believe that the immune system becomes “confused” after it is affected by either a virus or bacteria. This infection later affects the joints and can spread to other parts of the body.
Symptoms
- You have more than one joint that is swollen. You can have small joints in your hands, wrists, or feet.
- Morning stiffness can normally last hours or even the whole day.
- You experience pain, swelling, and stiffness in your elbows, wrists, hands, knees, neck, feet, and jaw. RA affects multiple joints.
Treatments
The types of medication recommended by your doctor depend on the severity of the symptoms and how long you have been affected. They include:
- Steroids are corticosteroid medications such as prednisone. They help in reducing inflammation, and pain, and slow joint damage.
- NSAIDs help in relieving pain and reducing inflammation. Examples are ibuprofen and naproxen sodium.
- Conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). They slow the progression of RA and also save joints and other tissues from being damaged permanently.
- Therapy. You can be referred to a physical or occupational therapist who can help you in exercising to keep your joints flexible.
In a case where medications fail, your doctor can opt for surgery to repair the damaged joints.
3. Gout
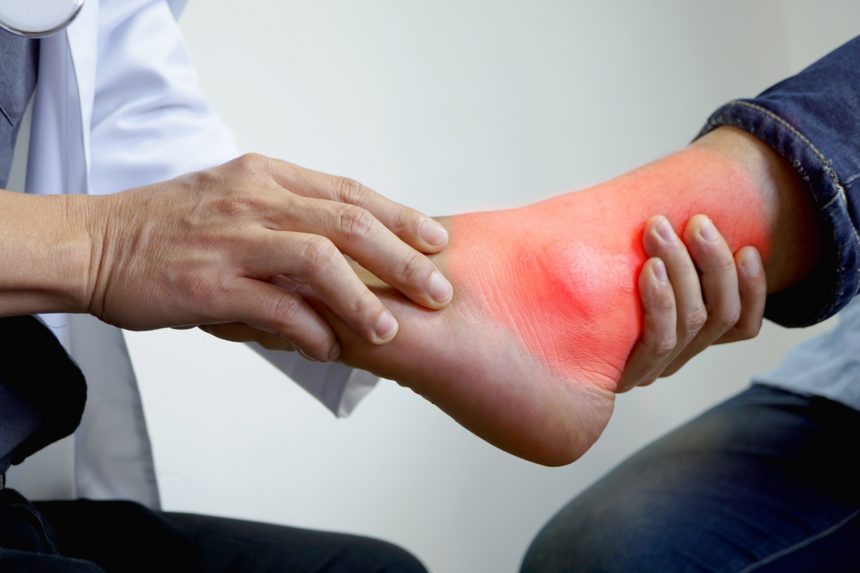
This is a situation where uric acid crystals build up in the joint. Most of the time it occurs in the big toe or any other part of the foot. There are two types of gout, that is primary and secondary.
Primary gout has no cause. It just happens. Secondary gout can be caused by chronic kidney disease or when you have used some medications, related to your kidney, for a long time. Other causes can also be being overweight, age, and family history.
When you are suffering from gout, you will often wake up with a sudden sharp pain in the big toe. This can happen after a night of drinking. Stress, drugs, and other illnesses can also cause this pain.
Gout occurs when your body is making more uric acid, you are eating a lot of food that raises uric acid levels or your kidneys are not in a position to process the uric acid made in the body.
Symptoms
- Inflammation and redness in the affected joints.
- Your range of motion is limited and you cannot move your joints normally.
- Intense joint pain especially in the big toe.
- Lingering discomfort in the joints.
Treatments
The doctor may prescribe medications such as:
- Colchicine. This is an anti-inflammatory drug that reduces gout pain.
- Corticosteroid medication such as prednisone to control pain and gout inflammation. They may be injected into your joint or can be in a pill form.
- NSAIDs relieve pain and control inflammation.
In a case where you experience several painful gout attacks, your doctor may recommend medications that will block uric acid production or medications that will improve uric acid removal.
4. Psoriatic Arthritis

This condition is caused by an inflammation of joints and skin (psoriasis). Psoriasis causes the areas of the inflamed skin to have scales. This usually affects the tips of the knees and elbows, navel, scalp, and areas around the anus or genital areas. Some people are only affected in one or a few joints.
This condition starts between the age of 30s and 50s but can also start in childhood. It is the skin disease (psoriasis) that shows up first.
Symptoms
- Swelling of the fingers and toes.
- Pitted or discolored fingernails.
- Lower back pains.
- Foot pains at the point where ligaments and tendons attach to the bones.
Treatments
There is no cure for psoriatic arthritis rather the treatment is for controlling symptoms and preventing the damage that may happen to the joints. If not treated, it can be disabling.
The doctor can prescribe the following:
- Conventional DMARDs slow down the progression of psoriatic arthritis and save tissues and other joints from permanent damage.
- A newer oral medication is Otezla to decrease the activity of an enzyme in the body thereby controlling the rate of inflammation within cells.
- NSAIDs reduce inflammation and relieve pain in cases of mild psoriatic arthritis.
Joint pain can make everyday tasks and activities unbearable. Severe ones can lead to disability. If you are experiencing the above joint pains or any other common ones, you can visit either a rheumatologist or an orthopedist. Both of them treat joint pain. However, the main difference is that a rheumatologist uses medication and other nonsurgical treatments while an orthopedist is a surgical specialist.
It is advisable that you seek guidance from your primary caregiver to know which specialist to go to.







