GHD is a rare condition when the pituitary gland is not secreted growth hormones. The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain and produces numerous hormones for body growth. The growth hormone or somatotropin controls cell growth and reproduction. Insufficient somatropin production by the pituitary may lead to a decrease in height. This is usually caused by severe brain injuries or other medical conditions.
GHD in childhood is categorized into congenital acquired, idiopathic, or all three. It can cause growth retardation, short stature, delayed maturation, and delay in lengthening bones. It is the most incongruent extremity to the chronological age.
- Congenital GHD, This type of GHD is visible from birth.
- Acquired GHD – GHD can also be acquired later due to trauma, infection, brain tumor growth, or Radiation Therapy.
- Idiopathic GHD- This is the third and most severe type of GHD. Unfortunately, there is no treatment for idiopathic growth hormone deficiency.
Now, after knowing about the growth hormone deficiency, it’s time to look forward to the signs and symptoms of GHD.
Signs & Symptoms For Childhood Onset

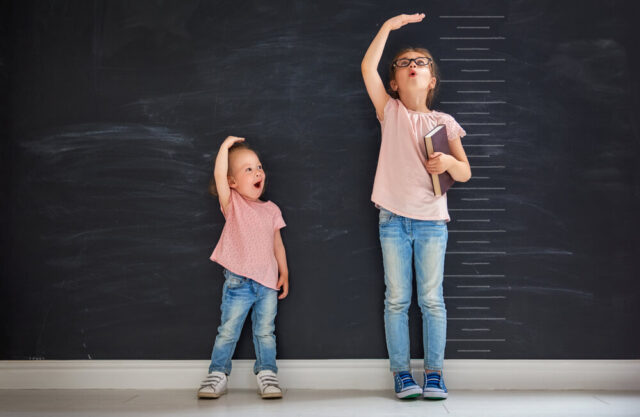
1. Height restriction
our child may be shorter than other children their age. This is an indicator that you have a somatropin disorder.
2. A child with a chubby appearance and a younger age
While your kid may have an average body, they may have GHD if they appear unnaturally chubby or have a smaller face than other children.
3. Late puberty
Your child’s puberty maybe later than expected, depending on the seriousness of growth hormone deficiency. Hypoglycemia and hyper exaggerated jaundice are the primary manifestations.
4. Micropenis
The condition of Micropenis is an incident sign of GHD. It becomes more severe as the baby gets older and leads to a growth deficit.
Signs & Symptoms For Adults Onset

Changes in body composition are one of the first signs that GHD has struck adults. These include an increase in fat near the abdomen and a decrease in strength and muscle mass. Low growth hormone levels are often accompanied by low mood, energy, depression, libido, sleep problems, and a decreased sense of well-being. Osteoporosis, an increase in the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, and osteoporosis can be long-term effects.
According to epidemiological data, growth hormone deficiency results in a decrease in life expectancy and nearly twofold higher mortality from cardiovascular disease. This is due to the development of atherosclerosis early in patients suffering from growth hormone issues.
5. Increased Body Fat
A low growth hormone may cause the reduced stimulation of lipolysis. This can lead to an increase in subcutaneous fat accumulation near the abdomen area. It can also increase visceral fat, which is a dangerous form of fat that builds up around the internal organs. This is more than an aesthetic problem. It can also be a severe health issue. This increases your risk of developing diabetes and heart disease.
6. Decrease In Muscle Mass And Strength
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), which can cause muscle loss and weakening, could be why. GHD patients often experience muscle loss, decreased physical strength, and reduced endurance. To prevent muscle loss, you can take Human Growth Hormone therapy, and it helps stimulate IGF-1 secretion and increases serum levels. One of the benefits of hch is that it has a muscle sparing effect and controls the loss of muscles. AGHD without the growth hormone’s protective effect can cause muscle weakness and loss. This can lead to unhealthful differences in body composition, especially when combined with abdominal fat gain.
7. Osteoporosis
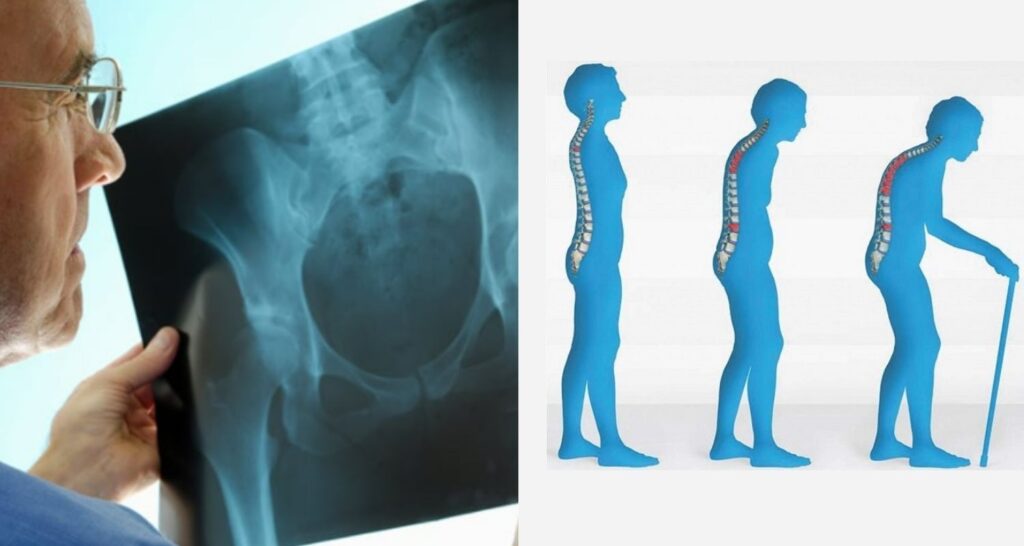
In normal circumstances, Human growth hormones have an anabolic impact on the bone tissue, which is controlled by IGF-1. Growth hormone insufficiently lessens this effect and accelerates the bone loss that occurs as we age. The result is a lower bone thickness and a higher chance of breaking.
HGH, as well as IGF-1, is essential for the growth of skeletal tissue throughout childhood as well as bone health in the later years of life. IGF-1 is the principal agent behind the anabolic effects of hormone growth. HGH increases its production in the bone tissue and within the liver.
IGF-1 stimulates specific kinds of bone-forming cells known as osteoblasts in the bone tissue. Additionally, GH has a direct effect on bone and decreases loss. The outcome is a higher bone mineral density and a lower chance of developing osteoporosis.
8. Reduced Sexual Desire
The HGH plays an essential role in sexual desire for women and men. HGH is essential in normal arousal levels and maintaining a normal sexual erection for males. Insufficient levels of HGH can cause insufficient sexual libido and other issues.
Adults with GHD frequently report a total absence of enthusiasm in their lives, energy levels, and enthusiasm for sexual activity. Both genders feel a constant sense of exhaustiveness and fatigue.
9. Impaired Quality Of Life

Patients with GHD are significantly less likely to have indicators for the quality of their lives, such as diminished psychological well-being, lower levels of energy, disrupted sexual life, and a higher degree of social solitariness contrasted with healthy individuals.
GHD causes many health issues like muscle loss and stomach fat accumulation that could affect your appearance. It can lead to discontent about your appearance and lower self-esteem, negatively impacting your overall health.
10. Sleep Problems Or Insomnia
Growth hormone deficiency is frequently associated with sleep-related issues like poor quality sleep and increased sleepiness during the daytime, and fatigue. These signs could be caused by a variety of hormonal changes that are associated with GH disorder.
GHD affects sleep quality by affecting certain stages of the sleep cycle. The people who suffer from GHD are less likely to get deep sleep and don’t sleep enough, even not feel rested or fresh after oversleeping. Sleep quality issues can have an adverse effect on your mood and social life.
Bottomline
The signs of a deficiency in growth hormone can impact your quality of life and the likelihood of living. If GHD is not treated, it may result in osteoporosis, atherosclerosis, and a rise in mortality from cardiovascular disease. Identify the symptoms at the initial stages and start your treatment accordingly.







