As the world continues to focus on sustainable waste management solutions, anaerobic digestion (AD) has emerged as a key technology for converting organic waste into renewable energy.
By breaking down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, AD produces biogas, which can be used for electricity or heat generation. While this process is highly effective in managing waste and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, it also presents a significant challenge: odour control.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of anaerobic digestion odour control, its impact on both environmental and social aspects, and how modern solutions are improving air quality at AD facilities.
For more information on the subject, check out this anaerobic digestion odour control case study.
The Challenge of Odour in Anaerobic Digestion

Anaerobic digestion involves the breakdown of organic material by bacteria in an oxygen-free environment.
While it produces valuable biogas, it can also generate unpleasant odours. These odours primarily come from volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, and organic acids, which are released during the breakdown of waste materials.
If not properly managed, these odours can pose a number of challenges for facilities operating anaerobic digestion systems:
- Local community impact: Persistent unpleasant odours can affect local residents, causing complaints, reducing the facility’s social licence to operate, and creating tension between the facility and the community.
- Health and safety risks: Certain gases, such as hydrogen sulfide, are toxic and can pose a serious risk to human health if inhaled in high concentrations.
- Regulatory compliance: Waste processing facilities must comply with environmental regulations that limit emissions of odorous compounds. Failure to do so can result in fines or even the suspension of operations.
This highlights the need for effective odour control strategies to ensure that anaerobic digestion facilities can operate efficiently while maintaining good relations with surrounding communities.
The Role of Odour Control in Sustainable Waste Management

Effective odour control plays a vital role in the overall success of an anaerobic digestion facility. Beyond just improving air quality, it also contributes to the facility’s sustainability by:
1. Enhancing public perception
Facilities that take proactive steps to manage odours are more likely to be accepted by local communities.
Demonstrating a commitment to environmental responsibility and public health builds trust and can mitigate resistance to the plant’s operation.
2. Ensuring regulatory compliance
In many regions, environmental agencies have strict regulations governing emissions, including odour.
By implementing robust odour control systems, AD facilities can ensure they remain compliant with local and national environmental standards, avoiding potential fines or sanctions.
3. Improving operational efficiency
When odours are effectively controlled, there is less risk of plant shutdowns, complaints, or forced mitigation efforts that could disrupt the facility’s day-to-day operations.
A smooth, continuous operation is essential for maximising the output of biogas and other valuable products.
4. Supporting air quality goals
Proper odour control also contributes to wider air quality management strategies.
By reducing the release of harmful gases, AD facilities help lower the overall levels of pollution, which can have far-reaching effects on environmental and public health.
Effective Anaerobic Digestion Odour Control Solutions

To mitigate the odours produced by anaerobic digestion, a range of strategies can be employed.
These solutions aim to reduce, eliminate, or neutralise the odorous compounds that escape from the facility. Some of the most common methods include:
1. Biological scrubbers
Biological scrubbers use microorganisms to remove odorous compounds from the air.
As the air passes through a biofilter, bacteria break down the VOCs, converting them into harmless by-products.
This natural process is environmentally friendly, energy-efficient, and highly effective in removing odours.
2. Activated carbon filtration
Activated carbon is a highly porous material that adsorbs odorous gases as air passes through it.
This method is commonly used in situations where biological scrubbers may not be practical or where additional odour removal is required.
Activated carbon filters are effective at removing a wide range of odorous compounds, including hydrogen sulfide and ammonia.
3. Chemical scrubbers

Chemical scrubbers use chemical solutions to neutralise odorous gases. These systems are typically used for more concentrated or harder-to-control odours.
Chemical scrubbers can be tailored to target specific odorous compounds, making them highly effective in reducing unpleasant smells at AD facilities.
4. Odour neutralisers
Odour neutralisers work by either masking or chemically neutralising odours.
While they may not remove the source of the odour, they can provide temporary relief and improve the overall air quality around the facility.
5. Odour monitoring and control systems
Real-time monitoring of air quality is an essential part of modern odour control strategies.
Automated systems can detect the concentration of odorous gases and trigger corrective actions when thresholds are exceeded.
By continuously monitoring air quality, facilities can respond quickly to any odour issues, minimising their impact on the surrounding area.
How Technology is Transforming Anaerobic Digestion Odour Control
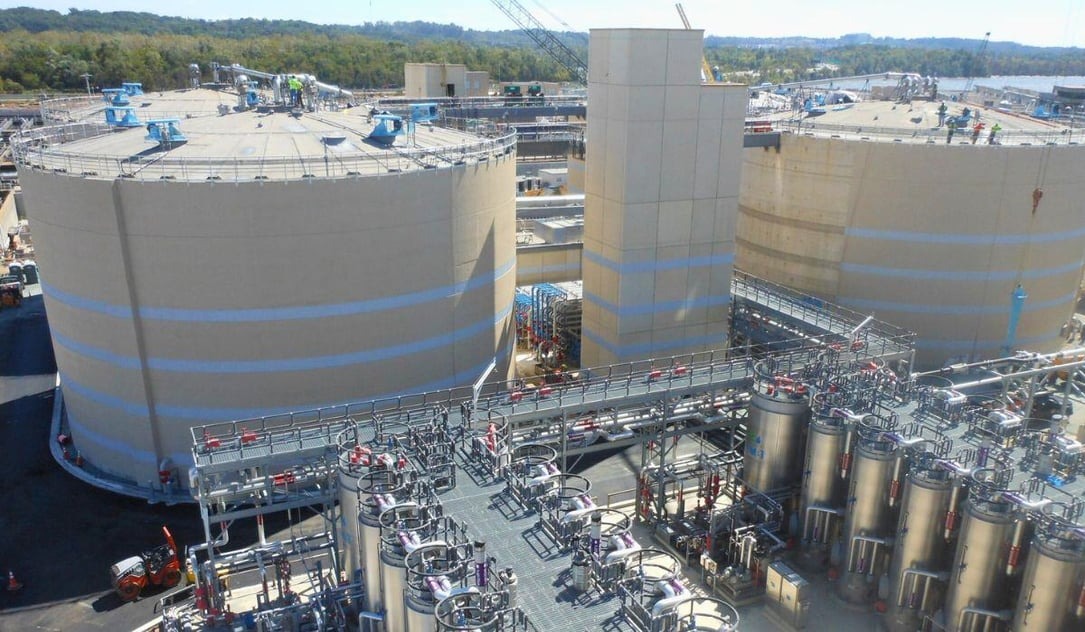

The development of advanced technologies has dramatically improved the ability to manage odour at anaerobic digestion plants.
New innovations and techniques continue to emerge, making odour control systems more effective and cost-efficient.
Data-driven odour management
The integration of data analytics into odour control systems allows for predictive maintenance and real-time optimisation of odour control measures.
By analysing trends in odour levels and operational parameters, facilities can identify potential issues before they escalate, reducing the risk of odour complaints.
Automation and AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of odour control systems.
AI algorithms can help predict when odour spikes might occur based on environmental factors and operational data.
Automated systems can then adjust odour control measures in real-time to prevent excess emissions, improving both efficiency and compliance.
Energy recovery from odour control systems
Innovative odour control systems now offer the potential for energy recovery.
For example, some biological scrubbers can capture and convert methane produced in the odour treatment process, which can then be used to generate electricity.
This makes odour control not only an environmental solution but also a potential source of energy recovery for the facility.
Case Study: Successful Anaerobic Digestion Odour Control
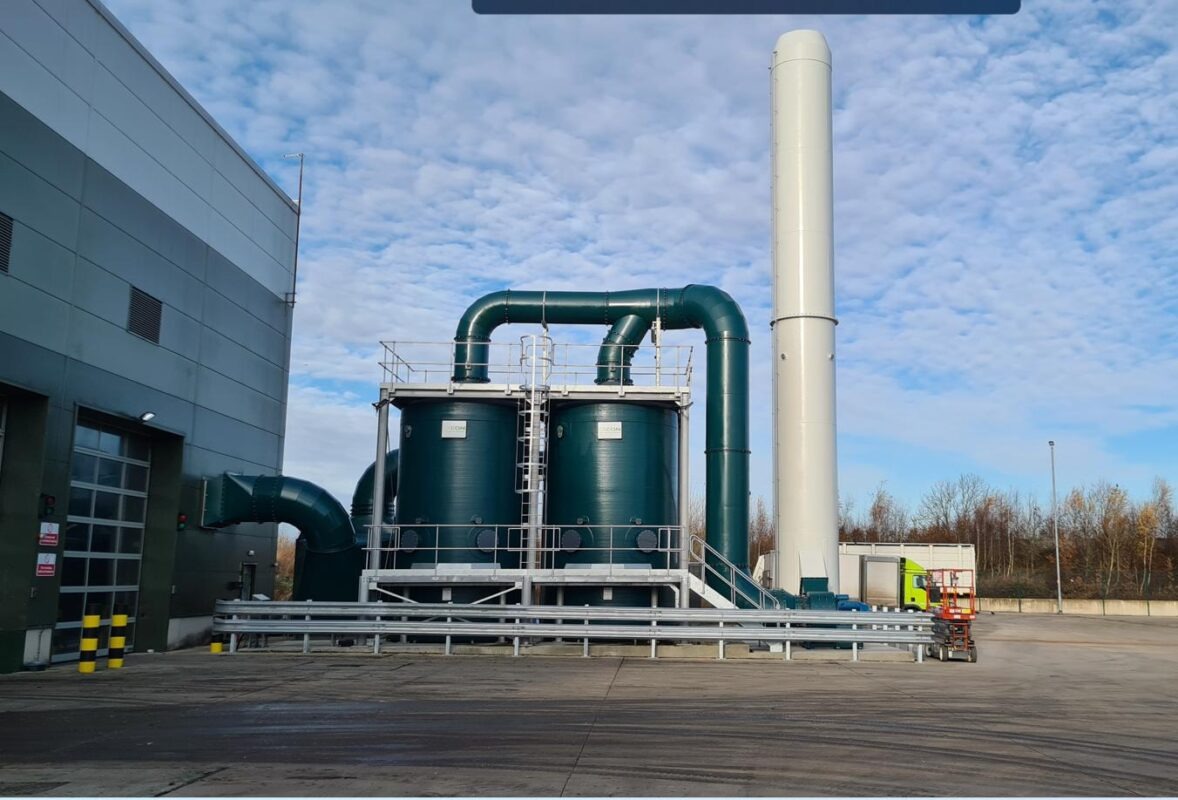

One excellent example of effective anaerobic digestion odour control can be seen in the case studies provided by Exeon.
They detail how advanced odour management strategies have been successfully implemented at various facilities, showcasing real-world applications of technologies such as biological scrubbers and AI-powered monitoring systems.
These case studies demonstrate the practical benefits of robust odour control strategies, highlighting the positive impact on both the environment and the facility’s operations.
You can read more in detail in the anaerobic digestion odour control case study.
Conclusion
Odour control is an essential aspect of running a successful anaerobic digestion facility.
With the right technologies and strategies in place, facilities can significantly reduce the negative impact of odours, ensuring compliance with regulations, protecting community relations, and enhancing operational efficiency.
As the industry continues to evolve, the adoption of advanced odour control methods will be key to maintaining the long-term success and sustainability of anaerobic digestion as a vital part of modern waste management.
For more information on the latest odour control technologies, explore the anaerobic digestion odour control case study by Exeon.